A collaborative study among the group of Lipids and Cardiovascular Pathology (IP: Vicenta Llorente Cortés) and Cancer Molecular Targets (IP: Pilar Navarro) from the IIBB- CSIC has shown that peptides which efficiently block modification of LDL aggregation, are capable of inhibiting intracellular cholesteryl ester accumulation in pancreatic tumor cells. LDLs (Low-density lipoproteins) are one of the main components of the dyslipemia, a risk factor for ductal pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PDAC), one of the most lethal cancers.
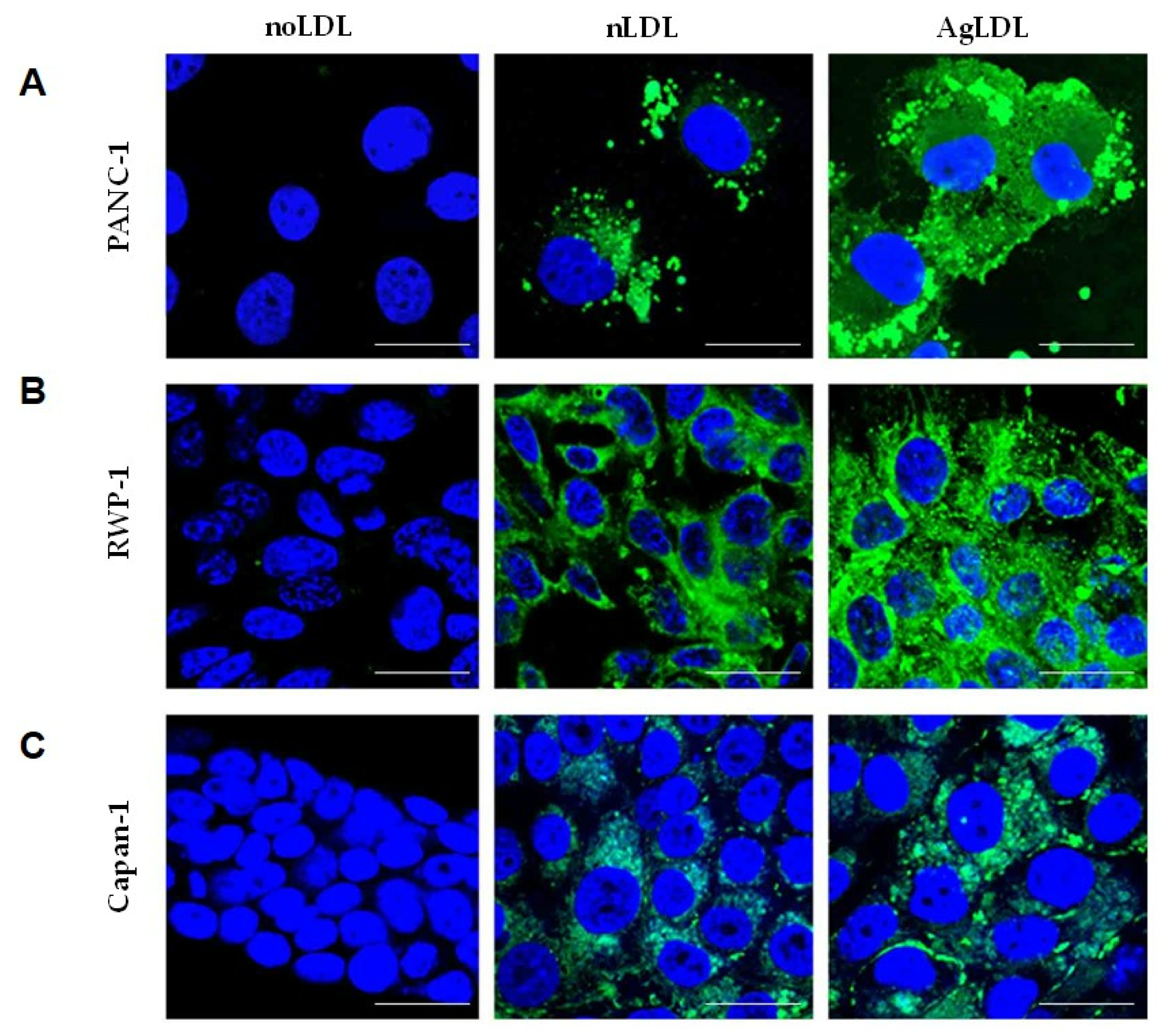
In the study, published in the journal Cancers (Basel), LDL particles modified with sphingomyelinase have been used. Using different human pancreatic cancer cell lines, the results indicate that LDL aggregates increase the intracellular concentration of esterified cholesterol and play a crucial role in the proliferation of pancreatic tumor cells. In addition, it has been shown that peptides that block the process of aggregation are highly effective in inhibiting not only the intracellular accumulation of cholesterol but also tumor proliferation. Thus, peptides that show anti-LDL aggregation properties may exhibit antitumor effects, opening a new avenue for the treatment of pancreatic cancer.
This study highlights the importance of cholesterol in the biology of pancreatic cancer and suggests that inhibiting its intracellular accumulation may be a new strategy against this aggressive tumor.
Image: Effects of nLDLs and AgLDLs on lipid droplet formation in pancreatic tumor cell lines. Confocal laser microscopy images show BODIPY-stained lipid droplets (green dots) and nuclei (blue) in the (A) PANC-1, (B) RWP-1 and (C) Capan-1 cell lines. Scale bar, 25 μm. LDL, low-density lipoprotein; nLDL, native LDLs; AgLDL, aggregated LDLs.
Article: Benitez-Amaro A, Martínez-Bosch N, Manero-Rupérez N, Claudi L, La Chica Lhoëst MT, Soler M, Ros-Blanco L, Navarro P, Llorente-Cortés V. Peptides against Low Density Lipoprotein (LDL) Aggregation Inhibit Intracellular Cholesteryl Ester Loading and Proliferation of Pancreatic Tumor Cells. Cancers (Basel). 2022 Feb 11;14(4):890. doi: 10.3390/cancers14040890. PMID: 35205638; PMCID: PMC8869901.
Financing: Fundación BBVA: Grants for research teams 2019.
https://www.fbbva.es/equipo/plaquechol-una-nueva-herramienta-para-predecir-el-riesgo-cardiovascular/